Lumbar Decompression
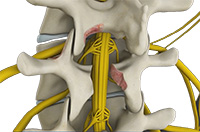
The spinal cord is protected by a bony column of vertebral bones, arranged one above the other. Injury or wear-and-tear can cause parts of the vertebrae to compress the nerves of the spinal cord, leading to pain, numbness or tingling in the part of the body that the nerve supplies. Lumbar decompression is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure over the compressed nerves in the lower spine (lumbar region). It is usually indicated in patients with herniated lumbar disc, spinal stenosis, spinal injury or spinal tumors, who have not found adequate pain relief with conservative treatment.
Lumber decompression is performed under general anesthesia. Your surgeon makes a small incision in the midline over your lower back. The layers of muscle are separated, and the affected nerve root is identified. The lamina (bony arch of your vertebra) may be removed (laminectomy) and the facet joints may be trimmed to reach the compressed nerve. Your surgeon removes any bone spurs or disc material that is pressing on the spinal nerve. The incisions are closed with absorbable sutures and covered with a dressing.
As with any procedure, lumbar decompression may involve certain risks and complications such as infection, bleeding, leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, bladder or bowel incontinence, weakness, numbness and pain.